Understanding Fat in Your Body 🤔 and the 6 Types
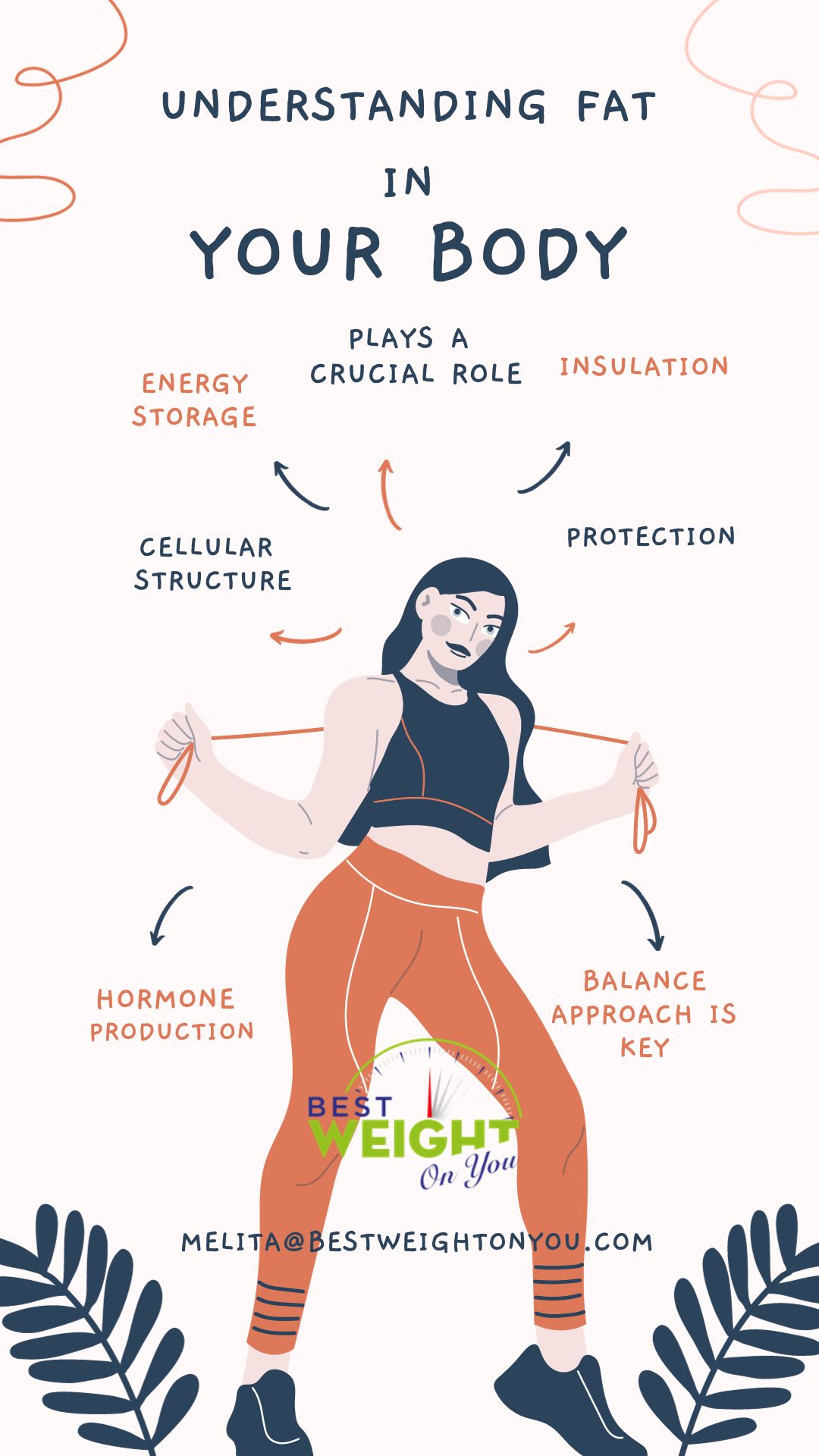
Fat is a natural substance with crucial roles in our body. Let’s break it down:
Chemical Composition 🧪: Fats are made up of fatty acids and glycerol, existing in various forms like saturated and unsaturated fats.
Energy Storage ⚡: Fat’s main gig? Storing energy as a concentrated source of calories, ready for action when your body needs a boost.
Insulation 🧤: Picture fat as your body’s cozy blanket. It helps regulate temperature, with adipose tissue (fat) providing insulation to keep you warm.
Protection 🛡️: Fat doubles as a shield, padding and safeguarding your organs. It acts like a cushion, preventing injuries and offering a protective layer.
Cellular Structure 🏗️: Fats play a vital role in cell membranes, maintaining cell integrity and functionality.
Hormone Production 🌐: Some hormones are fat-derived and pull crucial strings in various bodily functions.
The Balance Game ⚖️
Now, here’s the scoop on having too much fat:
Weight Gain 🍔: Overeating? Excess calories get stored as fat, leading to weight gain, making joints work extra hard.
Heart Problems ❤️: Too much of the wrong fats, like saturated and trans fats, can spike cholesterol levels, posing risks for heart diseases.
Type 2 Diabetes 🩸: Extra body fat, especially around the belly, links to insulin resistance and a higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
Joint Issues 🦴: Carrying extra weight stresses joints, increasing the chance of conditions like osteoarthritis.
Sleep Apnea 😴: Obesity heightens the risk of sleep apnea, where breathing takes a rollercoaster ride during sleep.
Liver Drama 🍺: Excessive fat in the liver can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), bringing serious health consequences.
Hormonal Rollercoaster 🎢: Fat cells can play tricks on your hormones, potentially causing irregular cycles and fertility hiccups.
Exploring Body Fat Types 🕵️♀️
-
Subcutaneous Fat 🍑
- Location: Just beneath your skin.
- Role: Energy reserve and insulation.
- Appearance: Soft and pinchable.
-
Visceral Fat 🍏
- Location: Around internal organs, especially in the abdomen.
- Role: Protects organs but excess can pose health risks.
- Appearance: Hidden, deeper within the body.
-
Brown Fat 🌰
- Location: Scattered among white fat, often in the neck and upper back.
- Role: Generates heat for body temperature.
- Appearance: Brown due to rich mitochondria.
-
White Fat 🍚
- Location: Distributed throughout the body.
- Role: Stores energy, produces hormones, and cushions organs.
- Appearance: Classic fat, storing calories.
-
Intramuscular Fat 🥩
- Location: Within muscle tissue.
- Role: Provides energy for muscles during activity.
- Appearance: Not easily visible, contributes to meat marbling.
-
Epicardial Fat 🫀
- Location: Surrounding the heart, between the heart and pericardium.
- Role: Provides cushioning for the heart.
- Appearance: Not visible externally but crucial for heart health.
Understanding these types helps us appreciate the diversity of body fat. While some fats are essential, maintaining a balance through a healthy diet and staying active contributes to overall well-being. 🌈💪
Let’s connect!
Schedule an appointment at your convenience or simply send me a message—I’m here to help in whatever way works best for you!
